Category: Uncategorized
Join MCT Group Limited at Metef Exhibition 2025!
- Home
- Join MCT Group Limited at Metef Exhibition 2025!

Join MCT Group Limited at Metef Exhibition 2025!
We are thrilled to announce that MCT Group Limited will be exhibiting at Metef 2025 from 5th to 7th March! Visit us at Stand B25, Hall 31 to explore our expertise in high-pressure die casting mold tool manufacturing and precision casting in Aluminum, Magnesium, and Zinc.
Metef is the perfect platform to connect, exchange ideas, and discover new opportunities in the die casting industry. Whether you need high-quality mold tools or precision casting solutions, our team is ready to discuss how we can support your projects.
Looking forward to meeting you there! Let’s shape the future of die casting together.
hashtag#Metef2025 hashtag#DieCasting hashtag#MCTGroup hashtag#Manufacturing hashtag#CastingSolutions hashtag#MoldTools hashtag#Aluminum hashtag#Magnesium hashtag#Zinc hashtag#Networking hashtag#Innovation
Unveiling the Role of Automotive Low-Voltage Connector Terminals in Intelligent Networking.
- Home
- Unveiling the Role of Automotive Low-Voltage Connector Terminals in Intelligent Networking.

Unveiling the Role of Automotive Low-Voltage Connector Terminals in Intelligent Networking.
The role of automotive low-voltage connector terminals in intelligent networking is pivotal for the efficient operation of modern vehicles. These connectors serve as the physical interface for electrical connections between various vehicle components, facilitating the exchange of data and power.
Data Transmission: Low-voltage connector terminals enable the transmission of data between different electronic control units (ECUs) within the vehicle. This includes communication between the engine control unit, transmission control unit, infotainment system, safety systems, and other onboard devices. By facilitating seamless data exchange, these connectors contribute to the integration of intelligent networking features such as advanced driver assistance systems (ADAS), vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, and vehicle-to-infrastructure (V2I) communication.
Power Distribution: In addition to data transmission, automotive low-voltage connectors play a crucial role in power distribution throughout the vehicle. They ensure that electrical power from the battery or alternator reaches various components, such as sensors, actuators, pumps, and motors. This is essential for the proper functioning of electronic systems that control vital vehicle functions, including propulsion, braking, steering, and comfort features.
Integration of Advanced Technologies: As vehicles become increasingly connected and autonomous, the demand for advanced technologies continues to rise. Low-voltage connector terminals facilitate the integration of these technologies by providing standardized interfaces for connecting sensors, cameras, LiDAR systems, radar units, and other components essential for autonomous driving and intelligent networking.
Reliability and Durability: Automotive low-voltage connector terminals must meet stringent reliability and durability standards due to the harsh operating conditions encountered in automotive environments. They must withstand exposure to temperature extremes, moisture, vibration, and mechanical stress while maintaining secure electrical connections. Additionally, connectors designed for intelligent networking applications must support high-speed data transmission and comply with industry standards such as CAN (Controller Area Network), LIN (Local Interconnect Network), Flex Ray, and Ethernet.
Scalability and Future-Proofing: As automotive technology continues to evolve rapidly, low-voltage connector terminals must be scalable and adaptable to support future innovations. Manufacturers must design connectors that accommodate increasing data bandwidth requirements, higher power demands, and emerging communication protocols. By investing in versatile connector solutions, automakers can future-proof their vehicles and ensure compatibility with upcoming advancements in intelligent networking.
In summary, automotive low-voltage connector terminals play a crucial role in enabling intelligent networking features in modern vehicles. From facilitating data transmission and power distribution to integrating advanced technologies and ensuring reliability, these connectors are essential components that underpin the functionality and connectivity of next-generation automobiles.
Why do we make a DFM report before making a mold for a plastic mold?
- Home
- Why do we make a DFM report before making a mold for a plastic mold?
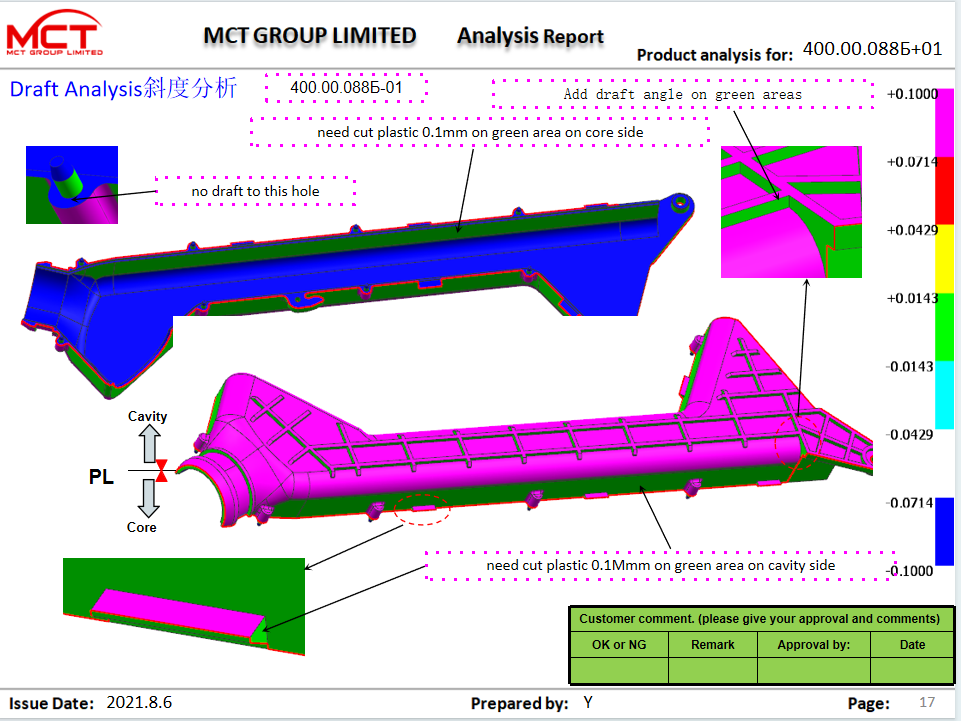
Why do we make a DFM report before making a mold for a plastic mold?
Stamping dies are specialized tools used in metalworking to shape or cut metal parts into specific forms. There are several types of stamping dies, each designed for different purposes:
Blanking Dies: These dies are used to cut flat shapes out of sheet metal. They work by shearing the metal along a defined outline.
Piercing Dies: Similar to blanking dies, piercing dies are used to punch holes through sheet metal. They can create simple round holes or more complex shapes.
Forming Dies: Forming dies are used to bend, stretch, or otherwise shape sheet metal into specific forms. They can be used to create bends, flanges, or other complex geometries.
Drawing Dies: Drawing dies are used to form sheet metal into three-dimensional shapes, such as cups or cylinders. They work by pulling the metal through a die cavity using a punch.
Progressive Dies: Progressive dies are a series of individual dies arranged in a sequence along a single strip of metal. As the metal strip moves through the dies, each operation is performed sequentially, allowing for the creation of complex parts in a single operation.
Compound Dies: Compound dies combine multiple operations into a single die. They are used to perform multiple operations, such as cutting, bending, and forming, in a single press stroke.
Trimming Dies: Trimming dies are used to remove excess material from a stamped part, often after it has been formed or punched. They can be used to trim edges or remove burrs.
Coining Dies: Coining dies are used to create precise, high-quality surface finishes on stamped parts. They can be used to add textures, patterns, or other features to the surface of a part.
These are some of the most common types of stamping dies, but there may be variations or specialized dies used for specific applications within metalworking industries.
What are the benefit of precision casting?
- Home
- What are the benefit of precision casting?
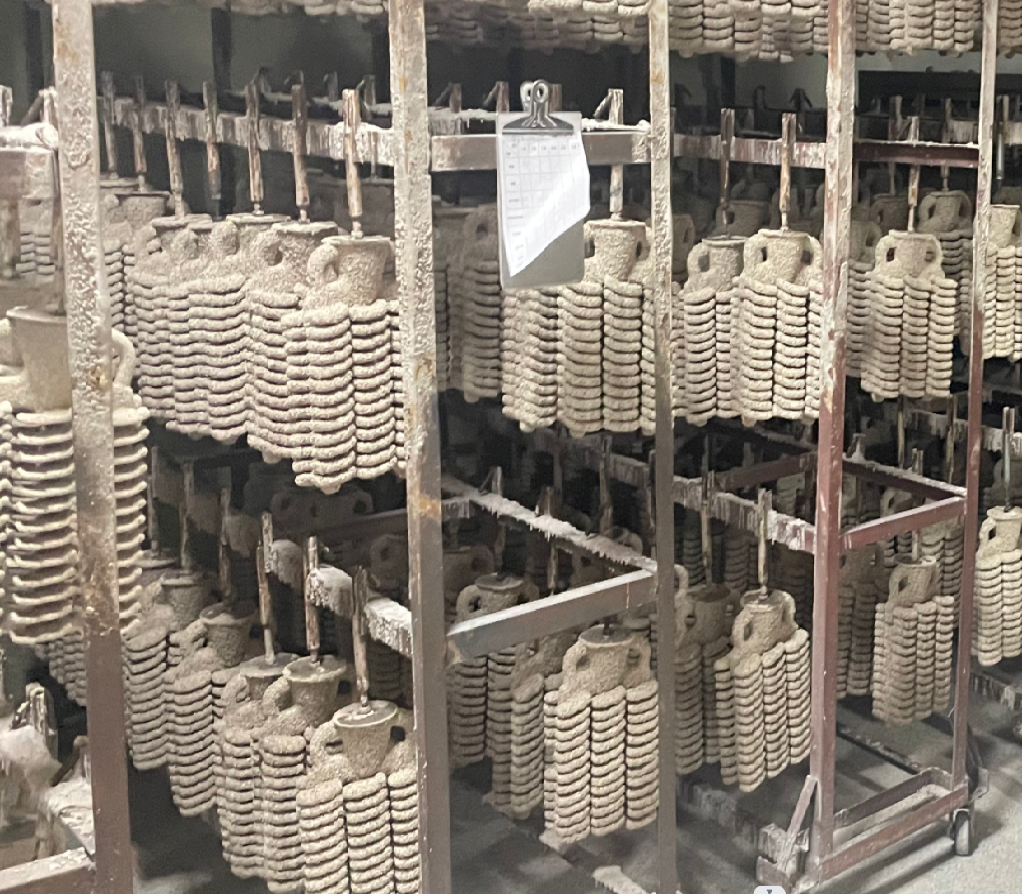

What are the benefit of precision casting?
Precision casting, also known as investment casting or lost-wax casting, offers several benefits in various industries. Here are some of the advantages of precision casting:
Complex Geometries: Precision casting allows for the production of complex and intricate shapes that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through other manufacturing processes. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where components often have intricate designs.
High Accuracy and Tolerance: The process enables the production of highly accurate and precise parts with tight tolerances. This is crucial in applications where precision is critical, such as in the manufacturing of medical devices or components for high-performance machinery.
Excellent Surface Finish: Precision casting produces parts with excellent surface finish and minimal post-processing requirements. This is advantageous in industries where smooth surfaces are essential, such as in the production of jewelry or components for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Material Flexibility: Precision casting supports a wide range of materials, including various metals and alloys. This versatility makes it suitable for producing parts with specific material properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, or heat resistance.
Reduced Material Waste: The process minimizes material waste since the mold material is reusable, and excess material can be melted and reused for other castings. This is an environmentally friendly aspect of precision casting.
Cost-Effective for Small Production Runs: While precision casting can be used for large-scale production, it is also cost-effective for small to medium production runs. This makes it an attractive option for industries that require flexibility in production quantities.
Near-Net Shape Production: Precision casting often produces near-net shape components, meaning that the final product requires minimal additional machining or finishing. This can lead to cost savings and reduced production time.
Design Flexibility: Engineers and designers have greater freedom in designing components with precision casting. The process accommodates intricate and complex designs, enabling the production of customized parts tailored to specific requirements.
Consistency and Reproducibility: Precision casting allows for the consistent and reproducible production of parts, ensuring uniform quality across multiple components. This is essential for industries that demand high reliability and consistency in their products.
Reduced Tooling Costs: Compared to other casting methods, precision casting can have lower tooling costs, especially for smaller production runs. This is because the process relies on a wax pattern rather than expensive molds or dies.
These benefits make precision casting a preferred choice in industries where high precision, complex geometries, and excellent surface finish are critical considerations.
What stamping dies are there?
- Home
- What stamping dies are there?

What stamping dies are there?
Stamping dies are specialized tools used in metalworking to shape or cut metal parts into specific forms. There are several types of stamping dies, each designed for different purposes:
Blanking Dies: These dies are used to cut flat shapes out of sheet metal. They work by shearing the metal along a defined outline.
Piercing Dies: Similar to blanking dies, piercing dies are used to punch holes through sheet metal. They can create simple round holes or more complex shapes.
Forming Dies: Forming dies are used to bend, stretch, or otherwise shape sheet metal into specific forms. They can be used to create bends, flanges, or other complex geometries.
Drawing Dies: Drawing dies are used to form sheet metal into three-dimensional shapes, such as cups or cylinders. They work by pulling the metal through a die cavity using a punch.
Progressive Dies: Progressive dies are a series of individual dies arranged in a sequence along a single strip of metal. As the metal strip moves through the dies, each operation is performed sequentially, allowing for the creation of complex parts in a single operation.
Compound Dies: Compound dies combine multiple operations into a single die. They are used to perform multiple operations, such as cutting, bending, and forming, in a single press stroke.
Trimming Dies: Trimming dies are used to remove excess material from a stamped part, often after it has been formed or punched. They can be used to trim edges or remove burrs.
Coining Dies: Coining dies are used to create precise, high-quality surface finishes on stamped parts. They can be used to add textures, patterns, or other features to the surface of a part.
These are some of the most common types of stamping dies, but there may be variations or specialized dies used for specific applications within metalworking industries.
How to eliminate the internal stress of plastic parts?
- Home
- How to eliminate the internal stress of plastic parts?
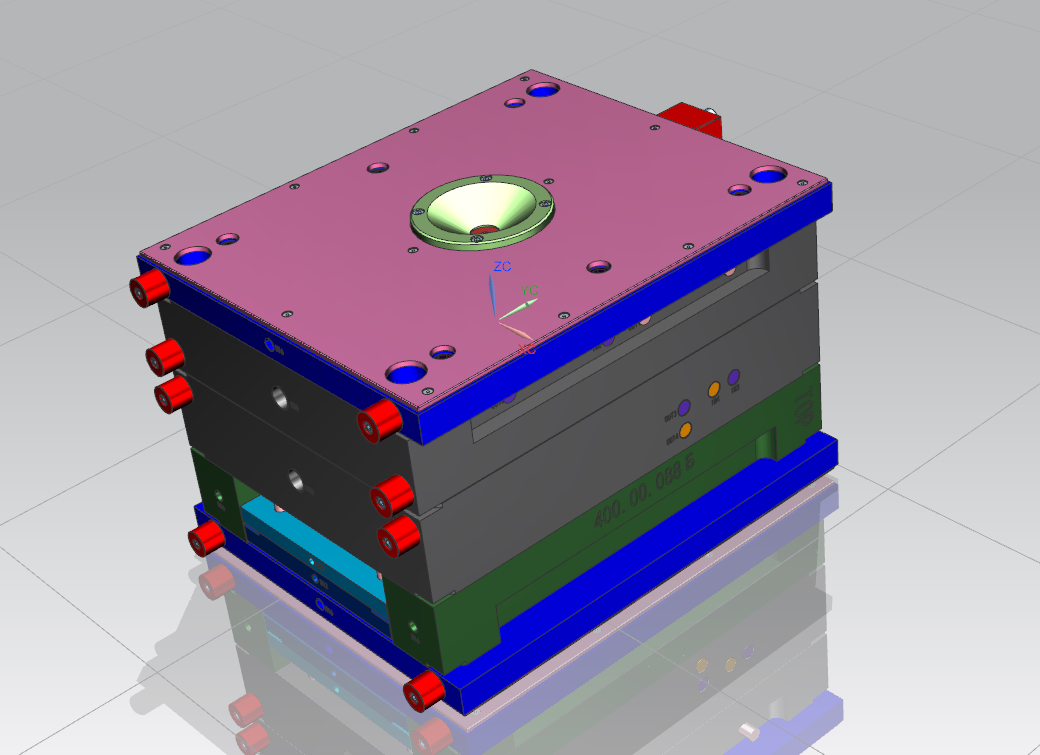
How to eliminate the internal stress of plastic parts?
Precision casting, also known as investment casting or lost-wax casting, offers several benefits in various industries. Here are some of the advantages of precision casting:
Complex Geometries: Precision casting allows for the production of complex and intricate shapes that would be challenging or impossible to achieve through other manufacturing processes. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace and automotive, where components often have intricate designs.
High Accuracy and Tolerance: The process enables the production of highly accurate and precise parts with tight tolerances. This is crucial in applications where precision is critical, such as in the manufacturing of medical devices or components for high-performance machinery.
Excellent Surface Finish: Precision casting produces parts with excellent surface finish and minimal post-processing requirements. This is advantageous in industries where smooth surfaces are essential, such as in the production of jewelry or components for the food and pharmaceutical industries.
Material Flexibility: Precision casting supports a wide range of materials, including various metals and alloys. This versatility makes it suitable for producing parts with specific material properties, such as strength, corrosion resistance, or heat resistance.
Reduced Material Waste: The process minimizes material waste since the mold material is reusable, and excess material can be melted and reused for other castings. This is an environmentally friendly aspect of precision casting.
Cost-Effective for Small Production Runs: While precision casting can be used for large-scale production, it is also cost-effective for small to medium production runs. This makes it an attractive option for industries that require flexibility in production quantities.
Near-Net Shape Production: Precision casting often produces near-net shape components, meaning that the final product requires minimal additional machining or finishing. This can lead to cost savings and reduced production time.
Design Flexibility: Engineers and designers have greater freedom in designing components with precision casting. The process accommodates intricate and complex designs, enabling the production of customized parts tailored to specific requirements.
Consistency and Reproducibility: Precision casting allows for the consistent and reproducible production of parts, ensuring uniform quality across multiple components. This is essential for industries that demand high reliability and consistency in their products.
Reduced Tooling Costs: Compared to other casting methods, precision casting can have lower tooling costs, especially for smaller production runs. This is because the process relies on a wax pattern rather than expensive molds or dies.
These benefits make precision casting a preferred choice in industries where high precision, complex geometries, and excellent surface finish are critical considerations.

